openFuyao v25.06 Released
New Feature of Multi-Core High-Density Scheduling Released, and Two Existing Features Updated
2025-07-02
The openFuyao community is dedicated to building an open software ecosystem for diversified computing clusters. We focus on promoting the efficient collaboration between cloud native and AI native technologies and maximizing the utilization of effective computing power. The community edition is designed based on a modular, lightweight, secure, and reliable philosophy. It is optimized based on the open-source Kubernetes platform and provides out-of-the-box containerized cluster management capabilities. It covers basic functions such as resource orchestration, auto scaling, and multi-dimensional monitoring, meeting O&M requirements of enterprise-level production environments.
This edition adopts the "core platform+pluggable components" architecture and provides various industry-level high-value components through the built-in application market. Its key capabilities include hybrid scheduling of intelligent and general-purpose computing power, unified management of heterogeneous resources, dynamic intelligent scheduling, and enhanced end-to-end observability. For AI and big data scenarios, it integrates the computing power affinity scheduling component that significantly boost the efficiency of data-intensive tasks.
With its "lightweight core+ecosystem enablement" mode, the openFuyao community edition empowers enterprises to quickly build efficient, elastic, and intelligent computing infrastructure and simplify O&M in heterogeneous environments, providing agile support for digital transformation.
openFuyao community edition 25.06 releases the multi-core high-density scheduling feature and enhances the colocation and Cluster-API features. The following describes the new and updated features.
New Feature
Multi-core High-Density Cluster Scheduling: Container Deployment Solution in High-Density Scenarios with 256 or More Cores
Multi-core high-density scenarios face challenges of surging lock contentions, unbalanced resource matching, and deployment density bottlenecks. To address these challenges, the community edition supports service type detection at the cluster layer, preventing I/O-intensive, memory-sensitive, and computing-sensitive services from being deployed on the same node.
The scheduling component at the multi-core high-density cluster layer detects the multi-core topology and optimizes the pod resource allocation policy, improving the container deployment density by 10%.
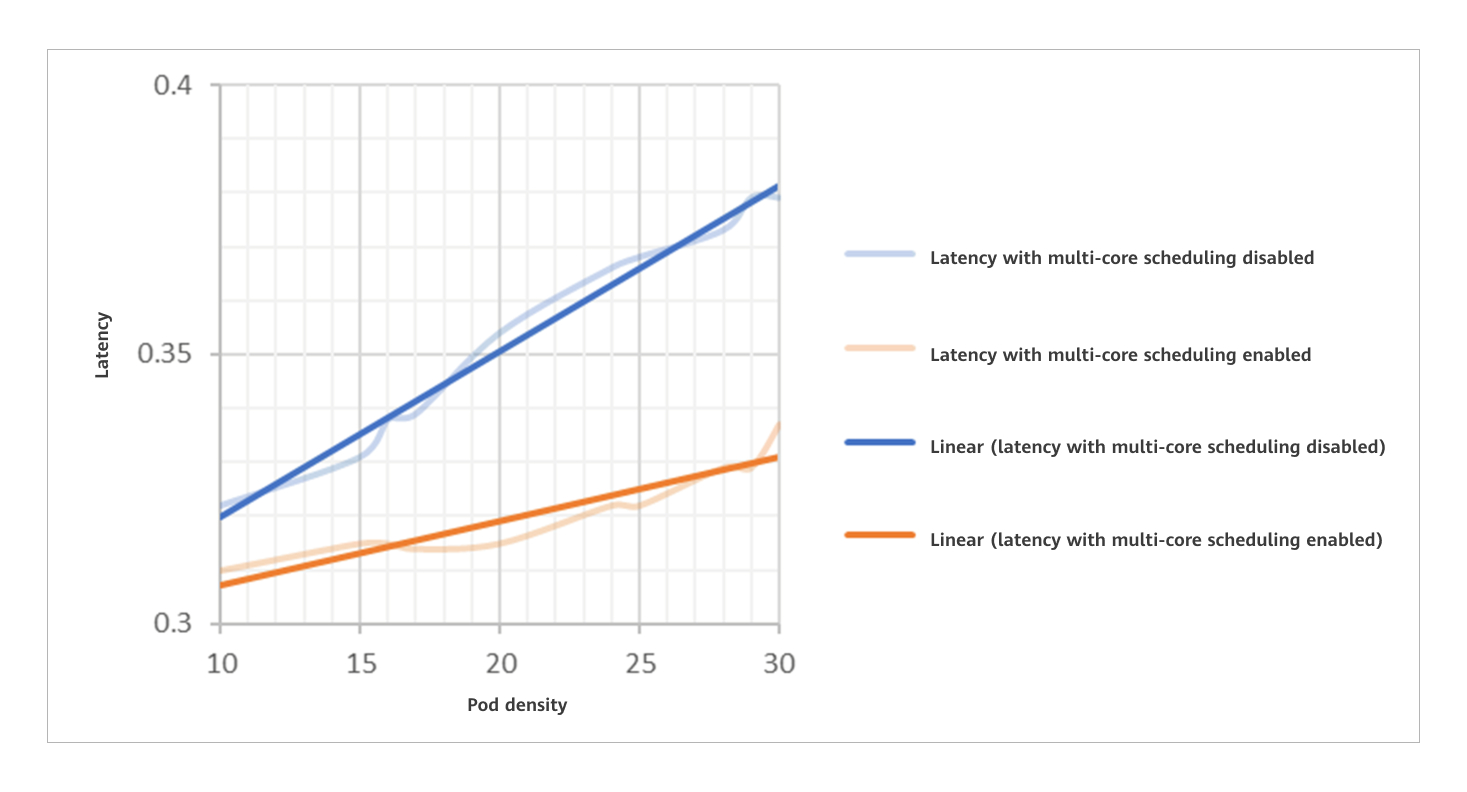
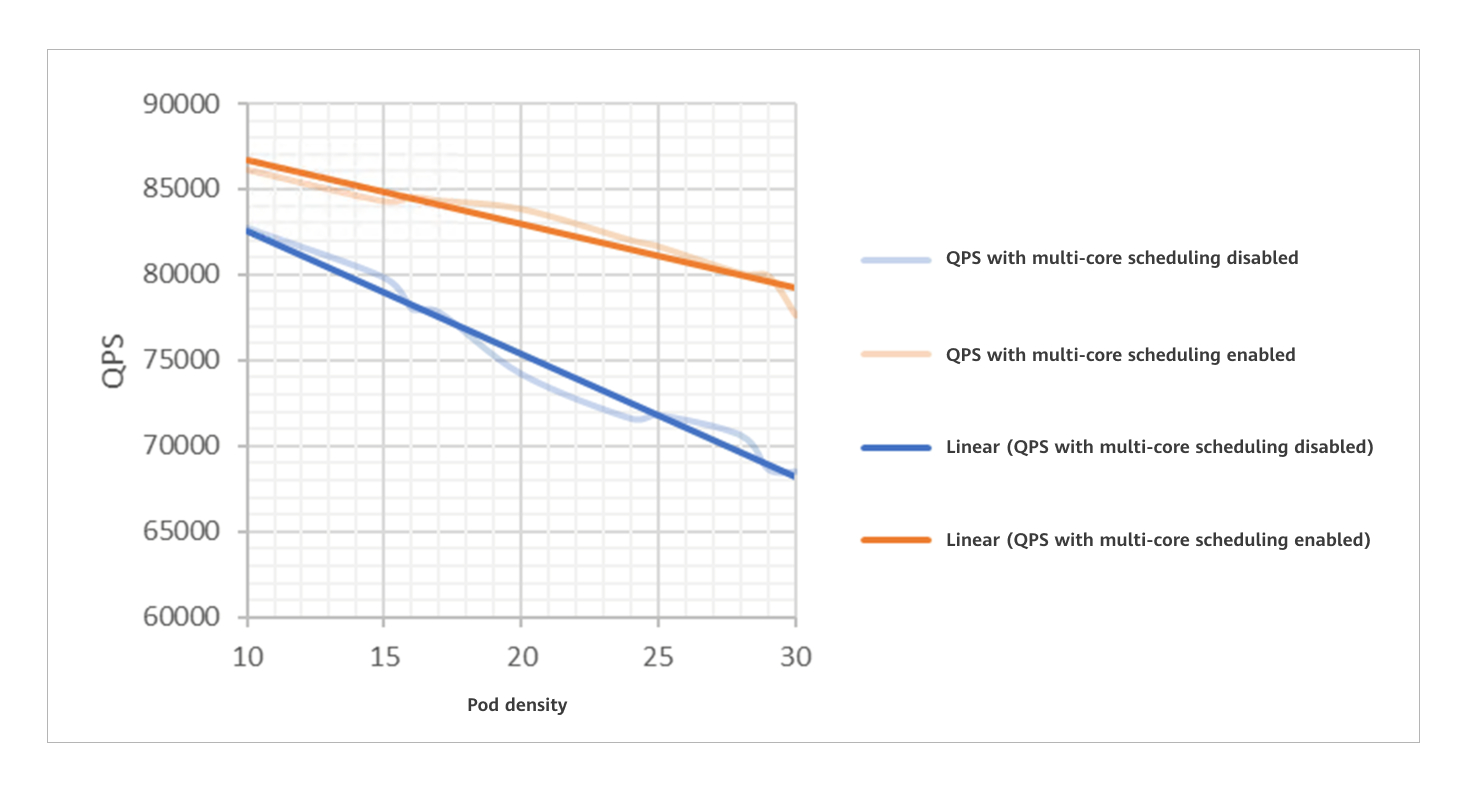
Two Major Updates
Colocation: Three New Levels of Workloads, Guaranteeing Online Services at a Fine Granularity While Optimizing Resource Utilization
In edition 25.06, three new levels of colocation QoS (HLS, LS, and BE) are defined to ensure service quality, improve functions such as priority preemption scheduling, load balancing scheduling of online services, and resource watermark eviction, and provide basic monitoring capabilities for colocation.
| QoS Type | Full Name | Characteristics | Scene | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HLS | High Latency Sensitive | There are strict requirements for latency and stability. Resources are not oversold and are reserved for greater certainty. | High-requirement online services | It is similar to the community's Guaranteed class. CPU cores are bound. The admission controller checks both CPU and memory requests and limits, ensuring that pods labeled HLS are treated as exclusive Guaranteed pods. |
| LS | LatencySensitive | Resources are shared, providing better elasticity for burst traffic. | Online services | It is a typical QoS level for microservice workloads, enabling better resource elasticity and more flexible resource adjustment. |
| BE | Best Effort | Resources are shared, with limited running quality. In extreme cases, resources are interrupted and evicted. | Offline services | It is a typical QoS level for batch jobs, providing stable computing throughput in a certain period of time at low cost. Only oversold resources are used. |
Enabling colocation can improve the CPU and memory usage by over 40% when the QPS decreases by no more than 5%.
Cluster-API: Optimized Installation and Deployment Time, Extended Operating System Compatibility
- In terms of installation efficiency, Cluster-API in edition 25.06 optimizes the installation and deployment tools. It merges the bootstrap node with the management cluster, streamlining the setup process for openFuyao. The time from installation start to service cluster availability is reduced by 40%.
- In terms of the installation scope, the installation package and openFuyao minimal set now support openEuler 20.03 LTS, openEuler 20.03 LTS SP3, and openEuler 24.03 LTS SP1, greatly expanding the application scope.
- In terms of usability, the pre-verification module is added to cluster lifecycle management. It helps prevent installation failures caused by incorrect node information when adding nodes to an existing cluster or creating a new one, thereby improving user experience.
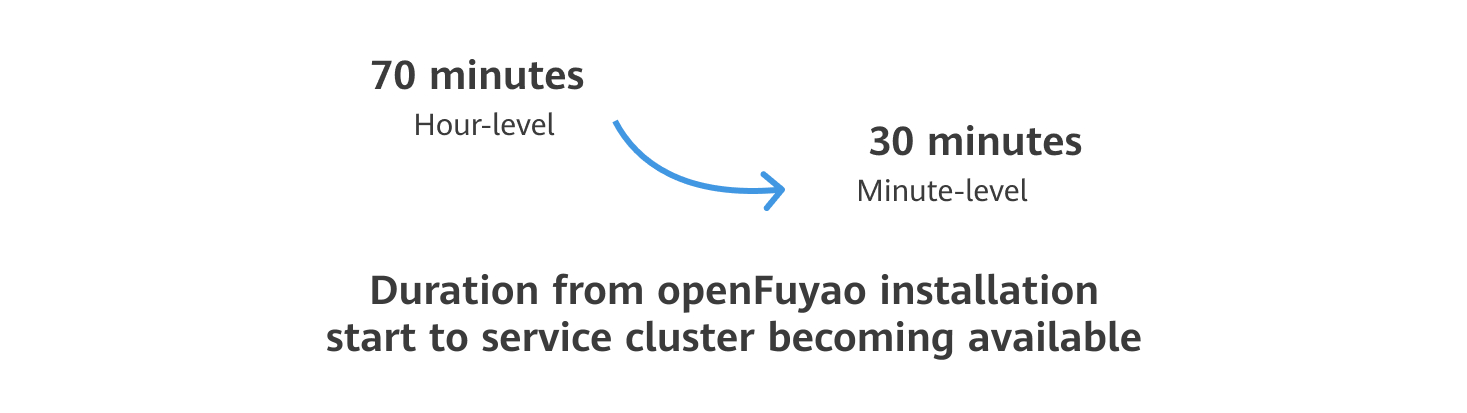
Updates in Other Features
- openFuyao Ray: Added the Ray monitoring panel to allow users to view cluster health information.
- NPU Operator: Added support for installation and deployment in offline scenarios.
Reference link: https://docs.openfuyao.cn/docs/v25.06/%E5%8F%91%E8%A1%8C%E8%AF%B4%E6%98%8E/%E7%89%88%E6%9C%AC%E4%BB%8B%E7%BB%8D/
This article is first published by the openFuyao Community. Reproduction is permitted in accordance with the terms of the CC-BY-SA 4.0 License.
